

Q.10 Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye.Q.9 Describe the construction of a kaleidoscope.(d) real, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object.

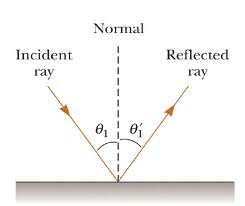
(c) real at the surface of the mirror and enlarged. (b) virtual, behind the mirror and of the same size as the object. (a) virtual, behind the mirror and enlarged. Q.7 The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.(d) Night birds have _ cones than rods in their eyes. (c) The size of the pupil becomes _ when you see in dim light. (b) If you touch your _ ear with a right hand in front of a plane mirror it will be seen in the mirror that your right ear is touched with _ (a) A person 1 m in front of a plane mirror seems to be _ m away from his image. Q.6 Fill in the blanks in the following.Q.5 Describe an activity to show that the incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal at the point of incidence lie in the same plane.(d) Marble floor with water spread over it Q.3 Mention against each of the following whether regular or diffused reflection will take place when a beam of light strikes.Does diffused reflection mean the failure of the laws of reflection? Q.2 Differentiate between regular and diffused reflection.Can you see objects in the room? Can you see objects out¬side the room ? NCERT solutions of related questions for Light
Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License. Use the information below to generate a citation. Then you must include on every digital page view the following attribution: If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a digital format, Then you must include on every physical page the following attribution:
If you are redistributing all or part of this book in a print format, Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Although the geometry of the proof is much more complex, corner reflectors can also be built with three mutually perpendicular reflecting surfaces and are useful in three-dimensional applications. Corner reflectors are a subclass of retroreflectors, which all reflect rays back in the directions from which they came. (For proof, see at the end of this section.) Such an object is called a corner reflector, since the light bounces from its inside corner. This is true whenever the reflecting surfaces are perpendicular, and it is independent of the angle of incidence. Corner Reflectors (Retroreflectors)Ī light ray that strikes an object consisting of two mutually perpendicular reflecting surfaces is reflected back exactly parallel to the direction from which it came ( Figure 1.9). The image appears to be behind the mirror at the same distance away as (b) if you were looking at your twin directly, with no mirror. The two rays shown are those that strike the mirror at just the correct angles to be reflected into the eyes of the person. The precise manner in which images are formed by mirrors and lenses is discussed in an upcoming chapter on Geometric Optics and Image Formation.įigure 1.8 (a) Your image in a mirror is behind the mirror. Mirror images can be photographed and videotaped by instruments and look just as they do with our eyes (which are optical instruments themselves). Although these mirror images make objects appear to be where they cannot be (like behind a solid wall), the images are not figments of your imagination. If the mirror is on the wall of a room, the images in it are all behind the mirror, which can make the room seem bigger. The angles are such that the image is exactly the same distance behind the mirror as you stand in front of the mirror. We see the light coming from a direction determined by the law of reflection. When you see yourself in a mirror, it appears that the image is actually behind the mirror ( Figure 1.8). (credit c: modification of work by Diego Torres Silvestre) (c) Moonlight is spread out when it is reflected by the lake, because the surface is shiny but uneven. Only the observer at a particular angle sees the reflected light. (b) A mirror illuminated by many parallel rays reflects them in only one direction, because its surface is very smooth. Figure 1.7 (a) When a sheet of paper is illuminated with many parallel incident rays, it can be seen at many different angles, because its surface is rough and diffuses the light.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
